Rib Cartilage Harvesting in Mumbai, India
The scientific world is leaping towards a new era with an age of corrective surgery or cosmetic surgery. It is usually done for various purposes, some might be medical and some might be cosmetic as well. The rib cage harvesting is one of the most efficient ways of reconstructing the nasal framework, which also happens to be the foundation of the secondary rhinoplasty. For this very purpose large quantity of cartilage is required for correction and shaping deformities and functional problems caused by previous procedures. The most successful and long-term results depend upon the grafts which have low resorption rates and adequate strength to offer a firm support. There are many potential donor sites and rib cartilage is one of them.
Cartilage is generally harvested from the eighth or the ninth rib or the conflux. If additional auricular cartilage requirement occurs, the tenth rib may also be harvested. If further requirement arises bone may also be harvested from the ninth rib if desired. The procedure involves a 4cm to 6cm incision overlying the eighth rib which also allows adequate exposure. A smaller incision is given to females, young patients, thin patients, and patients without breast implants. The intercostal muscles are less sturdy in the case of female patients than males. Thinner patients however have less subcutaneous itssue fat which makes a smaller incision feasible. In older patients, calcification occurs which might require a bigger incision. Patients with breast implants can undergo rib cartilage harvesting, but various technical modifications are essential to protect the integrity of the breast implant.
Rib cartilage harvesting has an added advantage, as it provides an abundant source of material to work with and essentially can be holistically utilized in revision Rhinoplasty as well as primary rhinoplasty. Rib cage harvesting is a pivotal art of the revision rhinoplasty s well and in addition, a lot depends on the surgeon, and how he has craved the ribs. Rib cartilage harvesting has become more complex, due to the more aggressive primary rhinoplasty techniques which are in practice.
The rib cartilage harvesting undergoes a certain set of procedures. The dissection further, proceeds through the rib perichondrium. The cutting of muscle fibers can be avoided and instead, they can be separated to reduce the postoperative pain. The usual dissection is done subprechondrially, the pleura is typically closely stuck to the perichondrium. When the graft is completely separated from the surrounding soft tissues, the graft is incised and delivered under direct vision. A malleable retractor might be planted by the surgeon beneath the rib as it is incised. Saline is also placed in the site of the surgery and positive pressure is applied to check any leakage if any. If any tear is observed in the pleura, a closure suture is done around a red rubber suction catheter. With the help of an anesthetist, the suture is tightened and the red rubber is removed. The whole process of placing the saline in the wound is again repeated to check for any further possibilities of bubbles. Hence, after comprehensive inspection, a standard, layered soft tissue closure without a drain is accomplished. In addition, skin edge eversion can be accomplished by everting subcutaneous sutures.
A radiograph of the chest is essentially taken in all the patients after the process of rib cartilage harvesting is completed. Every patient deals differently however silicon sheeting is recommended for the first 6 months after the surgical procedure. Some patients may have a little difficulty or discomfort for a couple of days initially with coughing. Overall the world of cosmetic and corrective surgery still offers a better and more contented life for patients in general.
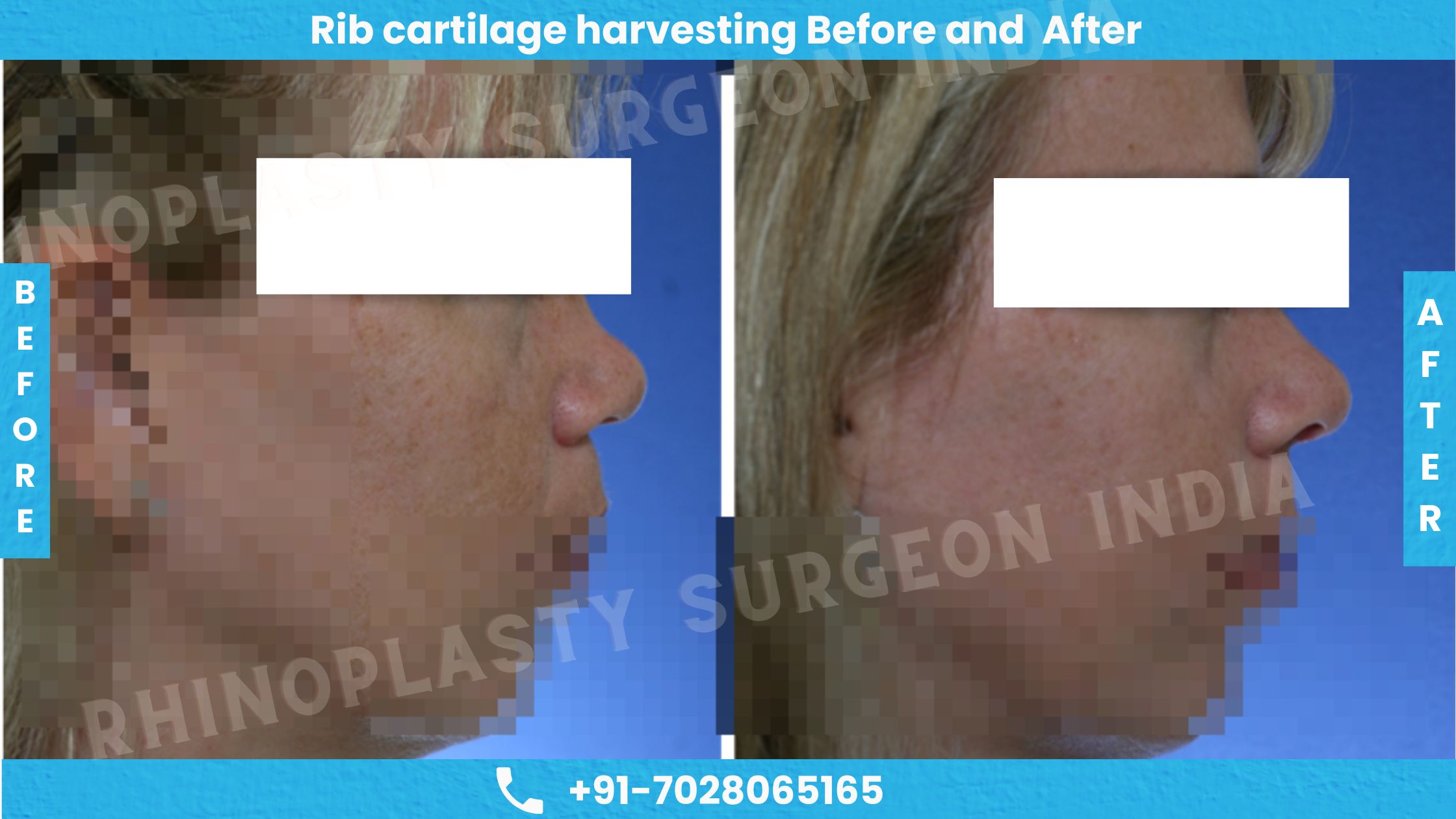
Before and After Photos of Rib Cartilage Harvesting
Frequently Asked Questions for Rib Cartilage Harvesting –
Question 1: How is rib cartilage harvested?
In order to harvest costal cartilage grafts, a skin incision is made along the anterior aspect of the rib, and both surfaces are circumferentially dissected using a curved and Doyen retractor. After being freed from the chondral junction, the bone is posteriorly sliced with bone-cutting forceps.
Question 2: Does rib cartilage removal hurt?
The discomfort often peaks in 3–4 days and then gradually lessens over the course of a week. Even while persistent chest pain months after surgery is uncommon after rib cartilage harvest, it is conceivable, especially if numerous rib cartilages were taken.
Question 3: What are the complications of rib harvesting?
The main disadvantages of rib harvesting are the challenges associated with patient compliance and wound care, postoperative pain, the potential for visual scarring, and the danger of pneumothorax.
Reference Link–
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5469241/#:~:text=%5B9%2C10%2C11%5D,posteriorly%20with%20bone%20cutting%20forceps.
- https://www.cedars-sinai.org/programs/microtia/patients/rib-cartilage-reconstruction.html#:~:text=Removing%20rib%20cartilage%20is%20painful,cause%20a%20chest%20wall%20deformity
- https://clinmedjournals.org/articles/jor/journal-of-otolaryngology-and-rhinology-jor-6-073.php?jid=jor