Auricular Perichondritis: Causes, Hospitalization, and Prevention
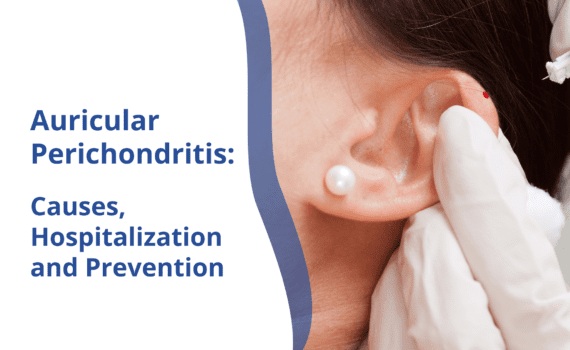
Auricular perichondritis is an ear infection that can make daily life uncomfortable. Perichondritis is an infection of the perichondrium. The perichondrium is a dense layer of fibrous connective tissue that covers most of the auricular cartilage in the body. If not treated in time, this infection on the ear can lead to a permanent ear deformity, a change in the shape of the ear, and a severe soft tissue infection.
What Causes Auricular Perichondritis?
The most common cause of this kind of infection is ear piercing, especially in the upper part of the ear, which causes damage to the cartilage. This often happens when the piercing is done by unlicensed practitioners and in unsafe conditions.
The Other Reasons Include
- Sports injuries, such as from boxing or other contact sports
- Previous ear surgeries
- Untreated middle or external infections
- Herpes zoster infection
- Trauma to the side of the head
- Burns
- Insect bites
- Acupuncture treatments
People who are suffering from previous inflammatory conditions, have a weakened immune system, or are suffering from conditions like diabetes are more susceptible to this kind of skin issue.
The bacteria responsible for this injection into the pinna is Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which also causes damage to the cartilage. Perichondritis, which causes infection of the cartilage, is a condition called chondritis.
In cases where the infection becomes severe, there can be blood collection at the site of the inflammation, and scar tissue formation can happen, leading to the cosmetic saddle nose deformity of the cauliflower ear. In extreme cases, auricular perichondritis can even cause nerve damage and tissue death, leading to permanent damage to the ear.
Symptoms Of Perichondritis
- Pain in the ear. It looks like a skin infection that worsens fast.
- Swelling
- Redness on the outer hair
- buildup of pus between ear tissue and cartilage
- Fever and fluid drain
How Is Auricular Perichondritis Diagnosed?
To get the right diagnosis, it is important to get the complete history of the patient and do a full physical examination.
- The diagnosis begins with the physical examination of the patient to check the ear condition.
- The next step is to check for the history of any recent trauma to the ears or the face. This includes information about recent upper ear piercings, grazes, burns, hematomas to the ear, lacerations, and acupuncture-like treatments.
- The next step is to check if the patient is suffering from any kind of hearing loss or sensation loss to the ear.
- If the patient is diabetic or taking any immunosuppressants, then they are more likely to develop rapidly spreading infections.
- If the skin rash spreads beyond the upper lip, then the infection might have spread beyond the ears.
Generally, the doctor might not ask for a routine blood test, but if the infection is spreading or if there is a swelling or abscess formation, then a blood test might be ordered.
Treatment for Auricular Perichondritis:
The treatment for auricular perichondritis depends on the severity of the condition.
- The first line of treatment is to start with antibiotics and corticosteroids to bring down the infection.
- If there is a lot of pus formation, then the surgeon will prescribe clearing the pus with a suction machine to drain the fluid and remove the dead skin and cartilage.
- If the infection spreads to other areas of the face or body, then oral steroids might be recommended as the line of treatment.
- If the infection has spread to the cartilage and cannot be treated conservatively, then it might be necessary to surgically remove the infected part of the ear.
You will need to remove all the foreign objects, such as ear piercings. Regular use of a warm compress is also recommended for the injected area. If necessary, pain relievers are also prescribed to help the patient.
Treatment for Cauliflower Ear
Repeated infections or frequent auricular perichondritis often lead to the formation of cauliflower year, which is because of the scar tissue formation and causes irregularities in ear shape.
It is often caused by a direct blow to the outer ear. Since the cartilage gets its blood supply from the skin, if there is an injury to the skin, the cartilage gets less blood and a lesser supply of necessary nutrients. This loss causes the tissue to become hard and change the shape of the ear.
Cauliflower ear surgery, also known as otoplasty or ear reconstruction surgery, is a procedure performed to correct deformities and irregularities caused by trauma or injury to the ear, leading to the development of the cauliflower ear. The surgery aims to restore the natural shape and contour of the ear, improving both the aesthetic appearance and functionality of the ear and getting relief from pain and infection.
Surgical procedure
The surgical technique used for cauliflower ear repair typically involves removing the excess tissue or cartilage in rhinoplasty, reshaping the ear, and reconstructing the ear’s natural contours. The surgeon may use various techniques, including cartilage grafting, suturing, and tissue manipulation, to achieve the desired results and restore the ear to its natural shape, which suits the facial features. Cauliflower ears need otoplasty within 30 days of initial clot formation; otherwise, ear cartilage grafts might become absolutely necessary.
Recovery
After the surgery for the cauliflower ear, you will be provided with specific post-operative instructions to follow, which may include keeping the head elevated, avoiding certain activities that could impact the healing process, and taking prescribed medications to manage pain and reduce the risk of infection. The patient might also need to wear a headband for a few days after surgery. Normal contact sports can be resumed about 12 weeks after the otoplasty. Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor your progress and ensure proper healing. In order to get good, natural-looking, long-lasting results, it is important to choose the best otoplasty surgeon for the same.
The best cure for auricular perichondritis is prevention. Here are some things that can help you with it:
- Avoid piercings in your high ear. These have a higher risk of infection than piercing your earlobe.
- If you have had an ear injury, then show it to the doctor immediately.
- Avoid contact sports, and if you have to play them, then make sure you take precautions to protect your ears, head, and nose.
- Try not to scratch your ears too much.